
|
|
INDEX: A measure of the relative average of a group of items compared to a given base value. Index measures are commonly used in economics to combine and compare diverse measures. One common type of index measure is for prices, such as the Consumer Price Index and the Dow Jones Industrial Average of corporate stock prices. Another noted type of index measure is to track macroeconomic activity, especially the index leading economic indicators. Indexes are usually weighted averages rather than simple arithmetic means that are measured relative to a base value or period. The Consumer Price Index, for example, measures the prices of consumer good, weighted by the quantities purchased. The value of a given period is then stated relative to a base year value, which generates a pure, "unitless" number in the range of 100 (give or take).
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           INTERCEPT, NET EXPORTS LINE: The intercept of the net exports line indicates autonomous net exports, net exports that do not depend on the level of domestic income or production. This can be thought of as net exports, exports minus imports, that the foreign sector undertakes regardless of the state of the economy. Autonomous net exports are affected by the net exports determinants, which cause a change in the intercept and a shift of the net exports line. | Net Exports Line | 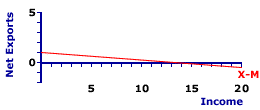
|
The net exports line shows the relation between net exports undertaken by the foreign sector and domestic aggregate income or production. The income and production measures commonly used are national income and gross domestic product.A representative net exports line is presented in the exhibit to the right. This red line, labeled X-M in the exhibit, is negatively sloped, indicating that greater levels of income generate greater net exports by the foreign sector. This negative relation indicates that imports, which are subtracted from exports to derived net exports, are induced by an expanding economy. The net exports line graphically illustrates the net exports-income relation for the foreign sector, which is then added to the consumption line to derive the aggregate expenditures line used in Keynesian economics to identify equilibrium income and production. The intercept of the net exports line indicates the intersection point between the net exports line and the vertical net exports axis. The net exports line intersects the vertical axis at a value of $1 trillion. Theoretically, this is a minimum "baseline" level of net exports, the amount of net exports undertaken if aggregate income falls to zero. It generally includes both autonomous exports and autonomous imports. This intersection indicates autonomous net exports--net exports unrelated to income. Click the [Intercept] button to illustrate. Autonomous net exports are net exports by the foreign sector that are unrelated to and unaffected by the level of income or production. This is best indicated by a zero level of income. For the aggregate economy autonomous net exports are mostly an unlikely theoretical extrapolation. However, from an analytical perspective, the intercept of the net exports line is affected by the net exports determinants. These are ceteris paribus factors other than income that affect net exports, but which are held constant when the net exports line is constructed. Any change in these determinants cause the net exports line to shift, which necessarily means a new intercept and a new level of autonomous net exports.

Recommended Citation:INTERCEPT, NET EXPORTS LINE, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2024. [Accessed: April 28, 2024].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
BROWN PRAGMATOX
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time browsing through a long list of dot com websites wanting to buy either a birthday greeting card for your aunt or a wall poster commemorating the moon landing. Be on the lookout for deranged pelicans.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
In the early 1900s around 300 automobile companies operated in the United States.
|

|
|
"The roots of education are bitter, but the fruit is sweet." -- Aristotle
|

|
PVCF
Present Value Cash Flow
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


